In the fields of advanced materials and high-end manufacturing, high-temperature vacuum heat treatment has evolved from a supporting process into a critical determinant of material performance limits and long-term stability. As process windows continue to narrow, even minor fluctuations can lead to significant deviations in final material properties. While the industry moves toward higher temperatures and stricter cleanliness requirements, a series of systemic challenges has become increasingly apparent. These challenges are rooted not in isolated failures, but in the underlying technical framework of vacuum thermal processing itself.
Drawing on CHJT’s long-term engineering experience in high-temperature, vacuum, and materials processing equipment, this article examines key control points, root causes, and future development paths from an industry-level perspective, with the aim of contributing to broader professional discussion. This deep technical insight is exactly what allows CHJT to manufacture high-precision custom design vacuum furnaces that meet the most rigorous thermal processing requirements of modern material science.
Under high-temperature vacuum conditions, equipment structures are continuously subjected to the combined effects of thermal stress, vacuum loads, and material aging. Unlike conventional thermal equipment, these influences rarely manifest as sudden failures. Instead, they appear as gradual performance degradation, such as declining vacuum retention, reduced sealing reliability at furnace doors, or irreversible deformation of internal supports and insulation systems.
From an industry standpoint, the root cause lies not simply in manufacturing accuracy, but in the significantly higher demands that high-temperature vacuum environments place on material selection, structural compatibility, and assembly processes. If thermal expansion compensation, material durability, and structural flexibility are not fully addressed during the design phase, problems tend to emerge cumulatively over long-term operation.
As a result, the industry is shifting from “post-operation correction” toward “design-stage control.” By differentiating sealing strategies between high- and medium-/low-temperature zones, releasing thermal stress through structural design, and incorporating component lifetime management into engineering calculations, long-term equipment stability can be established on a foundation of engineering rigor rather than empirical adjustment. By applying these rigorous standards, CHJT ensures that every high temperature furnace in its portfolio delivers exceptional thermal uniformity and reliability for the most demanding industrial applications.
Within high-temperature vacuum heat treatment systems, vacuum and control subsystems are among the most complex—and most frequently underestimated—components. Common industry issues such as vacuum instability, declining pumping speed, or control disturbances are rarely caused by single-component failures. Instead, they arise when increasing system complexity is not matched by corresponding upgrades in maintenance and management strategies.
Traditionally, vacuum performance has been treated as an equipment condition indicator rather than a core process parameter. However, as material sensitivity to oxygen content and atmosphere stability increases, this perception is changing. Vacuum level, pump operating status, valve reliability, and control system immunity to interference are now recognized as decisive factors for process success.
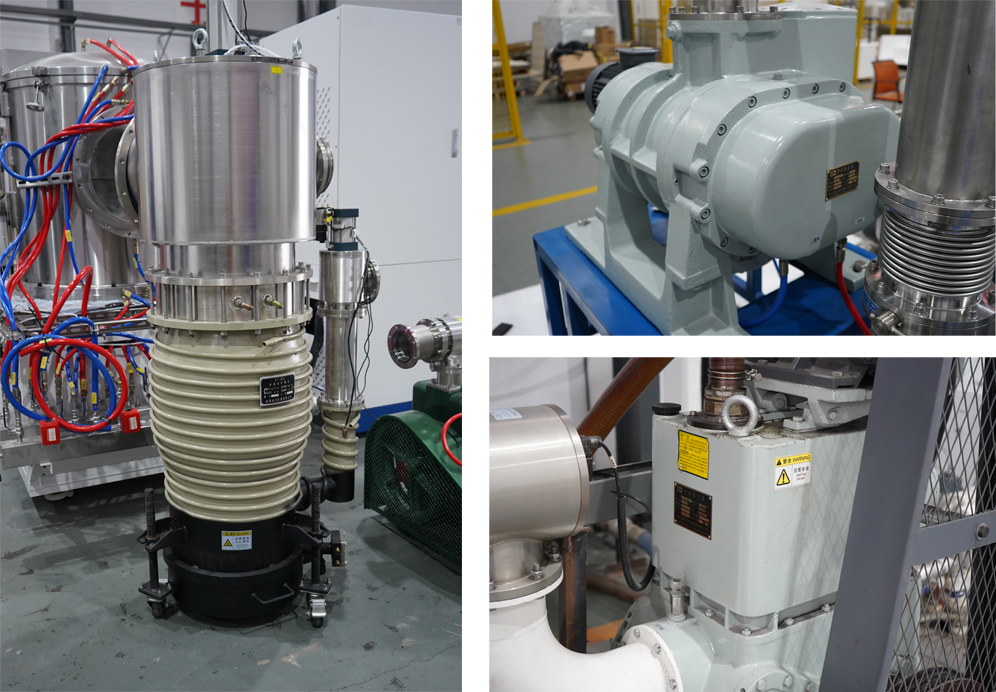

Equipment Pump Unit
Industry experience shows that only through systematic condition monitoring and logic interlocks—bringing vacuum deviations and temperature anomalies into early-stage automatic protection and alarm mechanisms—can risks be contained before they escalate into batch scrap or uncontrolled downtime.
Compared with mechanical or electrical issues, temperature field uniformity and process repeatability are less visible but play a decisive role in whether vacuum heat treatment can truly support high-end manufacturing applications.
“Inconsistent results within the same batch or between different runs” is a common industry phenomenon. In many cases, the root cause is not incorrect parameter settings, but systemic coupling between thermal design, loading configuration, and cooling pathways. As process windows become increasingly narrow, experience-based adjustments alone are no longer sufficient.
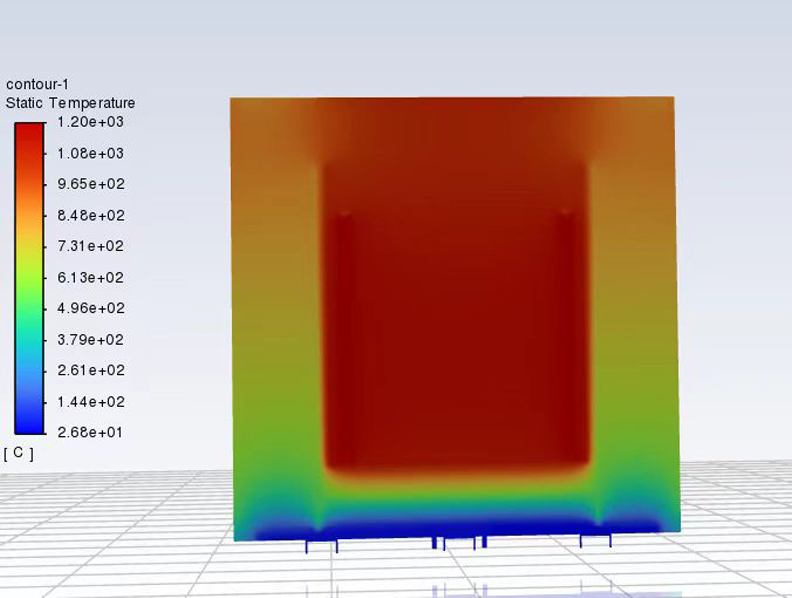
Vacuum Heat Treatment Equipment Temperature Simulation Diagram

Hydrogen Degassing Furnace Temperature Simulation Diagram
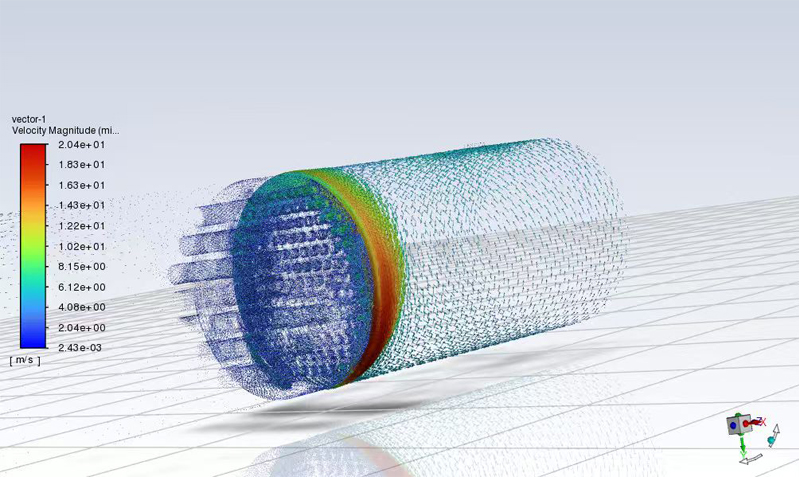
Single-arm Carbon Nanotube CVD Furnace Temperature Simulation Diagram
Consequently, industry consensus is gradually forming around several fundamentals: multi-zone independent temperature control, periodic temperature uniformity surveys, and standardized loading practices. In parallel, the use of simulation tools to validate thermal fields and cooling behavior at the design stage is becoming a preferred approach for reducing uncertainty in advanced applications.
As investment levels and system complexity of high-temperature vacuum equipment continue to rise, the industry increasingly recognizes that total cost and delivery capability are determined less by initial purchase price and more by unplanned downtime and process instability throughout the equipment lifecycle.
Traditional maintenance models based on manual inspection and reactive repair can no longer meet modern requirements for continuity and consistency. These are being replaced by data-driven lifecycle management approaches. Continuous monitoring and trend analysis of key parameters—such as vacuum, temperature, power, and energy consumption—enable early identification of performance degradation and a shift from reactive response to planned intervention.
With further integration of digital platforms, analytical models, and remote diagnostics, vacuum thermal equipment is evolving from a passive processing tool into a system-level platform with state awareness, risk prediction, and process coordination capabilities. This transformation marks a broader industry shift from equipment-centric thinking toward lifecycle value and system reliability.
In CHJT’s view, the core challenges facing the high-temperature vacuum heat treatment industry are not isolated technical issues, but the management of uncertainty arising from growing system complexity.
Sustainable solutions depend on long-term understanding of industry pain points, continuous refinement of engineering details, and sustained investment in automation, digitalization, and intelligent technologies. Built on years of engineering practice, CHJT approaches vacuum thermal processing from a system-engineering perspective, continuously advancing the industry toward greater stability, controllability, and intelligence.


